8 secure data entry practices for banking and financial services

A typical bank processes thousands of information daily. This includes data related to customer onboarding, transaction recording, loan processing, and trade and investment among others. Most of these are highly sensitive and require confidentiality & security.
But the task of data entry is prone to error, so much so that there is even a term for it: fat-finger. Inaccurate or incorrect data entry can have costly consequences. Deutsche Bank paid a US hedge fund $6 billion [Source: Marketwatch] as a result of a fat finger, which it recovered but not without much embarrassment. Citi Bank, which likewise wired $900 million to some hedge funds, was not as lucky—it could not have its money back [Source: Bloomberg].
Need for Secure Data Entry Practices
The increasing complexity in banking & finance and the rising reliance on technology have introduced even more vulnerabilities. As data becomes more critical and central to businesses and individuals, data security will attract more attention. At the same time, customers and regulators are demanding more stringent privacy and data protection.
This calls for a need to take data security more seriously and adopt safe data entry practices.
So, we have outlined here some of the best data entry practices to securely enter data and maintain their integrity, thus preventing data leakage and seepage of errors into uncorrupted data. These practices will ensure that you have control over the integrity of data and that a costly mistake is not required to open your eyes to see the right path forward.
Secure Data Entry Practices for Banking and Financial Services Sectors
There are plenty of practices banks and financial institutions can adopt to maintain data integrity—and thus their credibility and reputation, and customers’ trust. Some of these are conventional wisdom such as educating and regularly training employees and setting up multiple-factor authentication methods. Others are more arcane and require expertise—like masking and randomizing data.
It is not possible, nor is it necessary, to discuss all these practices. So here we’ve distilled the eight most important data entry practices that you can follow in the banking and financial services industry.
8. Role-based Access Control
Role-based access control (RBAC) restricts admission to data and systems based on the roles and responsibilities of individuals within the organization. Assigning specific rules and permissions to users and granting access only to information necessary for their tasks reduces the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive information, including mishandling, potential data breaches, and leakage of data. RBAC also enforces segregation of duties, preventing any single user from having excessive control over critical processes. This prevents conflicts of interest and fraud.
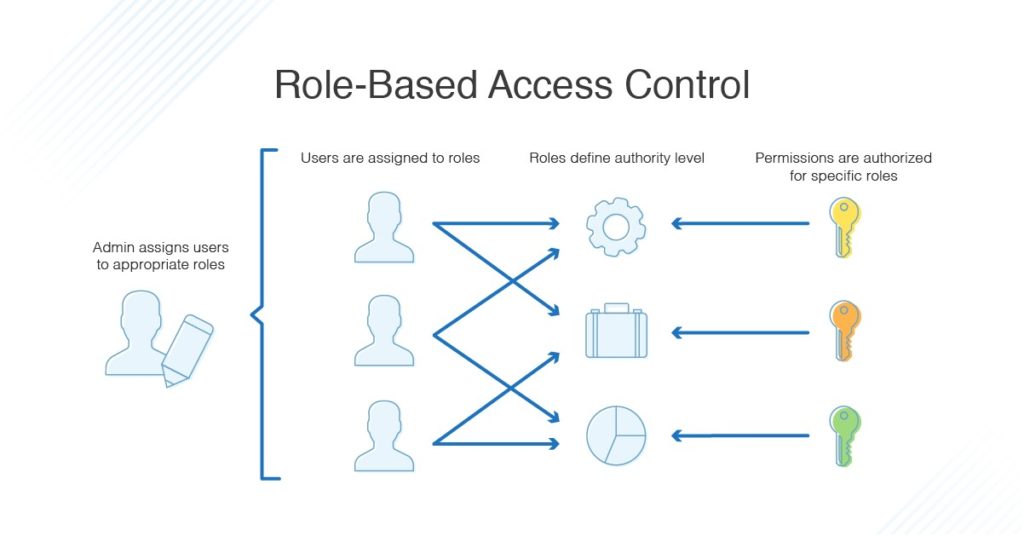
[Source: Dnsstuff]
The use of RBAC to manage user privileges within a system has other benefits besides securing data. According to a report [Source: Nist] prepared for the National Institute of Standards and Technology, RBAC reduces employee downtime, increases efficient provisioning, and enables more efficient access control policy administration.
7. Classifying Data by Sensitivity Level
Classifying data according to their sensitivity and limiting their access is another best practice to secure data and prevent sensitive data from getting into the possession of unwanted individuals. This ensures that different types of data receive the appropriate level of protection and access controls based on their importance and potential risk.
The sensitivity of data can be classified into levels such as restricted, high, moderate, and low. More granular classification may be used depending on the needs and size of the organization. This will decrease data misuse and breaches but at the cost of introducing unwanted bottlenecks.
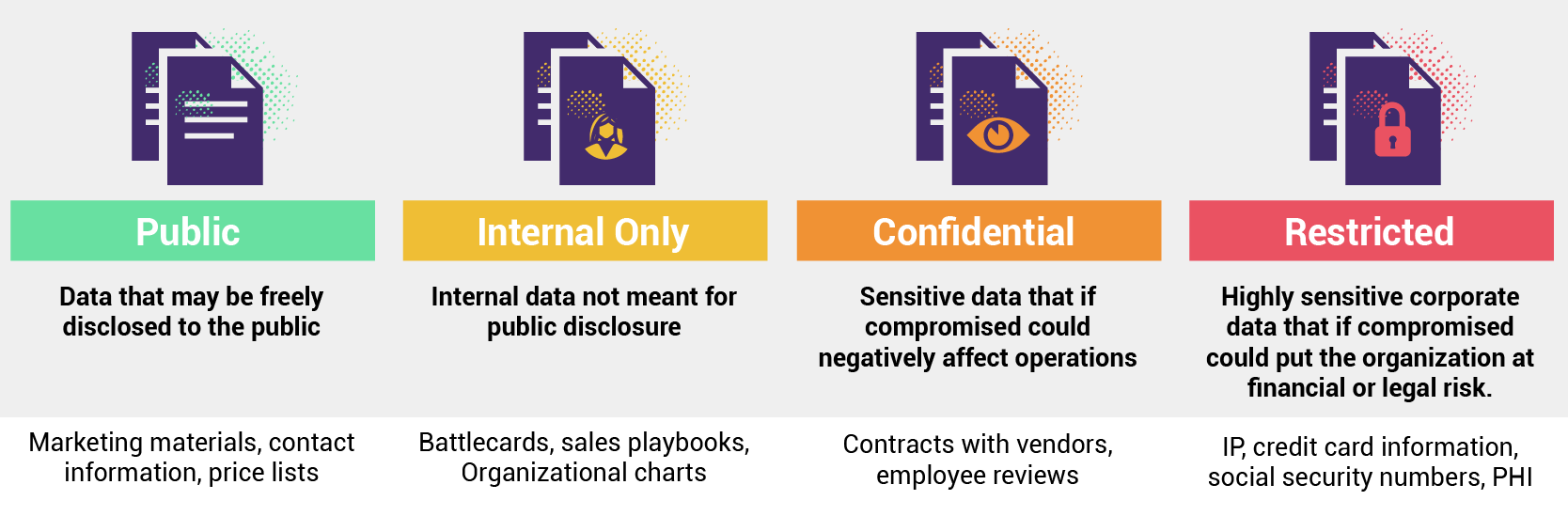
Data classification according to their sensitivity | [Source: Dasera]
Proper classification enables banking and financial services companies to implement appropriate encryption mechanisms and security measures based on data categories. This will help reduce data storage costs by removing the need to encrypt all data. It also helps ensure that vendors and third parties, to whom data may be shared, handle them with appropriate security measures.
6. Adopting Encryption Protocols
To preserve the integrity of data, encryption is a vital practice whose value cannot be overstated. Adopting encryption protocols such as SSL/TLS is critical. Encryption, especially asymmetrically [Source: Cloudflare], ensures that only authorized parties can access the data, providing a crucial layer of protection against unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyberattacks.
Encrypting data at rest—those stored on devices, servers, or databases—or in transit—data being transported between two networks or devices—prevents unauthorized access in case physical devices are lost, stolen, or improperly disposed of.
Encryption also ensures that the storage and handling of data are compliant with data protection regulations such as GDPR [Source: Endpointprotector] and HIPAA [Source: Hipaajournal], which, though they do not explicitly mandate encryption, stress the need for ensuring it.
5. Data Auditing and Logging
Data auditing and logging provide a means to track, monitor, and analyze activities related to data access, entry, and manipulation. Implementing robust auditing and monitoring mechanisms will enable tracking and recording of all data access and changes. This will facilitate in identifying suspicious and malicious activities, and the activities flagged immediately.
You can also quickly assess the source and impact of a breach by analyzing the audit trail—a series of audit logs—which will enable you to take immediate action. By reviewing audit logs, system administrators and security teams can track user activity and investigate security breaches, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
This also has the added advantage of establishing individual accountability and reduces the risk of data breaches either due to negligence or mischief.
4. Error Checking and Validation
The above practices are necessary to ensure data security, integrity, and accuracy but they are not sufficient. Despite our best efforts at eliminating manual errors, they happen. We are humans after all; all too human, in fact. Hence, implementing some error-checking mechanisms during data entry must not be taken for granted.
Humans are not just prone to making mistakes; they’re also poor at spotting them. Have multiple people review the data, especially if the information is critical.
Data validation is imperative. It ensures that the data are reliable and trustworthy. Validation processes can help identify and prevent the entry of duplicate data, reducing confusion and inefficiencies caused by redundant records.
Errors in data entry can have more severe consequences, such as financial losses, operational disruptions, and reputational damage. Validation can help reduce these risks.
3. Data Anonymizing and Randomization
Anonymizing personally identifiable information is essential to protecting customers’ privacy. Data anonymization allows information to be transferred across a boundary, such as between two departments within an organization or between two organizations while ensuring that information remains confidential.

Anonymizing and pseudonymizing remove personally identifiable information | [Source: Statice]
Pseudonymizing or randomizing data can help reduce data misuse without reducing data utility. This also ensures that organizations can store data in a way that is compliant with regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR, which stipulates that data on people in the EU undergo either an anonymization or pseudonymization [Source: Europa] process.
2. Disabling Copy-paste Functionality in Data Entry Forms
Convenient as copying and pasting information from one source to another, it is not conducive to data integrity. Convenience always comes with a price, and in data entry, the price can be costly. For example, allowing information to be copied and pasted would make it easy to maliciously copy sensitive information and use it for nefarious purposes.
Disabling the functionality can thus reduce the risk of data leakage or unauthorized sharing. And not only that, copy-pasting data between different applications can introduce errors, especially if the formats or structures are not consistent. It can also lead to duplication of data and replication errors.
Disallowing copy-paste will also help enhance the quality and accuracy of the data being entered as it prevents users from bypassing data validation checks that are in place.
1. Confidentiality Agreement with Outsourcing Partners
Outsourcing menial and mundane tasks such as data entry has allowed banks and other financial institutions to cut costs and increase output. This practice has thus become a staple of most organizations. However, outsourcing is not without pitfalls.
Giving third parties access to sensitive data is fraught with risks. They may have less stringent data security and privacy policies in place, and there may be less oversight. This is why some practices outlined above are crucial to protecting data integrity. But no less important is establishing a confidentiality agreement with outsourcing partners.
A confidentiality agreement outlines the responsibility of the outsourcing partner to maintain the security and secrecy of the data they handle and establishes liability in the event of a security breach. More important, though, is to choose partners wisely and enter into agreements with trustworthy data entry service providers that have a track record of maintaining confidentiality and have tangible signs of trustworthiness such as ISO certification.
Conclusion
Data entry remains an essential component, especially in the banking and financial services sector. Data entry at first glance seems menial and unimportant but it is hugely consequential. It can often introduce weak links in the chain of data security unless taken due caution and best data entry practices kept in place.
Data outsourcing companies fill this gap, helping firms take care of their data entry needs without having to worry about data compromisation while at the same time maintaining a fat profit margin.










